

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 12, Pages: 1321-1327
Original Article
Kayode I Adenuga1*, Noorminshah A Iahad2, Suraya Miskon2
1Faculty of Enterprise, Creative and Professional Studies, Farnborough College of Technology, Farnborough, United Kingdom
2Information Systems, Azman Hashim International Business School, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor Bahru, Malaysia
*Author for correspondence
Kayode I Adenuga
Faculty of Enterprise, Creative and Professional Studies, Farnborough College of Technology, Farnborough, United Kingdom
Email: [email protected]; [email protected]
Received Date:07 April 2020, Accepted Date:23 April 2020, Published Date:08 May 2020
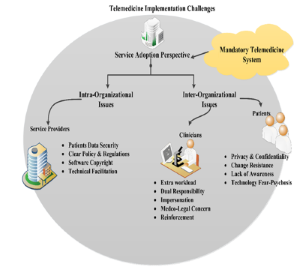
Objectives: The study seeks to understand why there is a wide gap in the telemedicine service implementation and adoption in Nigeria, the existing evidence shows that less than 5% of such hospital information systems has been utilized in a country of more than 180 million people. Methodology: We applied in-depth semi-structured interviews approach such that the opinions of clinicians were sampled at two government hospitals in Nigeria to identify other principal users' attributes affecting telemedicine implementation adoption from clinicians' perspectives. The combination of the factors from literature and thematic analysis led to the formulation of telemedicine service adoption framework that highlights telemedicine implementation issues. Findings: The outcome of the study led to the establishment of a telemedicine implementation framework and recommendations for a feasible and sustainable telemedicine service adoption for clinicians in Nigeria.
Keywords: Telemedicine; Adoption; Implementation
Copyright: © 2020 Adenuga, Iahad, Miskon. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.