

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v17i25.1484
Year: 2024, Volume: 17, Issue: 25, Pages: 2658-2666
Original Article
Pegadapalli Ashok1∗, Haleem Unnisa2, Rama Udai Kumar3, M Chenna Krishna Reddy1
1Department of Mathematics, University College of Sciences, Osmania University, Hyderabad, 500007, Telangana, India
2Department of Mathematics, DR.V.R.K Women’s College of Engineering &Technology, Moinabad, 500075, Telangana, India
3Department of Mathematics, Keshav Memorial College of Engineering, Ibrahimpatnam, 501510, Telangana, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:02 May 2024, Accepted Date:03 June 2024, Published Date:25 June 2024
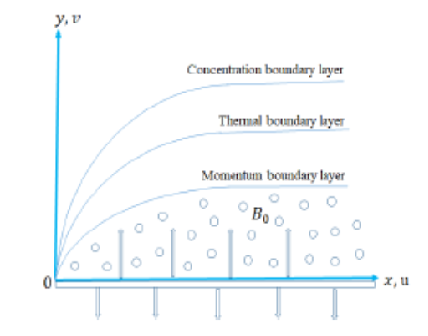
Objective: The research focused on Williamson's nonlinear governing flow on Magneto hydrodynamic incompressible, steady fluid over a porous stretching sheet in a two-dimensional direction. The permeable stretching sheet embedded by Williamson fluid is based on the flow model of non-Darcy Forchheimer law with chemical reaction. This article concentrated on an energy equation dominated by the dissipation parameter analysis. Methods: The governing mathematical partial derivative formulations are changed to a system of ordinary differential formulations with appropriate similarity transformation. The mathematical formulations are evaluated employing the numerical method of the R-K fourth-order scheme. MATLAB software bvp4c is used for computing numerical results. The numerical results and graphs were successfully demonstrated with the R-K fourth-order system. Findings: For the influence of Williamson non-Newtonian, non-fluid observed emerging dimensionless quantifiers such as Williamson number, porous, electric, thermophoresis, Brownian motion, Prandtl, and Schmidt dimensionless number respectively. The performance of non-dimensional parameters is investigated in detail. Novelty: As described in the results, Williamson's non-Newtonian nanofluid under the influence of magneto-hydrodynamics is mentioned as a new value to the existing literature. The gained results are the innovative study of the influence of chemical reaction on Williamson non-Newtonian nanofluid and magnetic strength and reported on dimensionless parameters.
Keywords: Electric parameter, Williamson Nanofluid, Darcy-Forchheimer, Viscous dissipation, Chemical reaction quantifier
© 2024 Ashok et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.