

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 16, Pages: 1693-1702
Original Article
Md. Rezaul Karim1∗, Tarikul Islam2 , Shubhajit Dutta1 , Alamgir Hossain1 , Sudipta Bain3
1 Department of Textile Engineering, Port City International University, Chittagong, 4225, Bangladesh
2 Department of Textile Engineering, Jashore University of Science and Technology, Jashore, 7408, Bangladesh
3 Department of Fashion Design and Technology, Uttara University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
∗Corresponding author:
Md. Rezaul Karim
Department of Textile Engineering, Port City International University, Chittagong, 4225, Bangladesh
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:13 April 2020, Accepted Date:29 April 2020, Published Date:10 June 2020
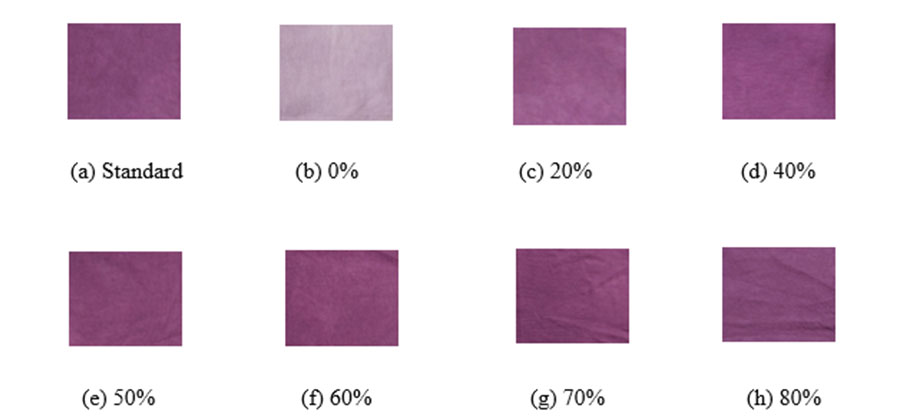
Objectives: To study the reuse of dye effluents in order to minimize the dyeing cost. Methodology: In this study, the exhausted dye effluents were reused into 7 new dyeing baths along with 7 different percentages of dyes and chemicals to evaluate the color fastness properties as well as shade difference. Firstly, the exhausted dye effluents were collected from the dye bath of the standard sample after dyeing was completed. Then respectively added extra 80%, 70%, 60%, 50%, 40%, 20% and 0% of the dyes and chemicals in the 7 different new baths where dye effluents of standard sample dyeing existed. After dyeing, all the 7 samples were collected and tested with ISO methods for the assessment of color fastness to Wash and color fastness to Rubbing. Moreover, all the samples were analyzed against the standard one with the help of a Spectrophotometer. Findings: From the overall testing reports, it had found that color fastness to wash and rubbing were satisfactory for all samples. But the CMC decision revealed that the sample which was treated along with the presence of an extra 80% dyes and chemicals in dye effluents showed minimum shade difference from the standard sample. So, it can be said that about 20% of dyes and chemicals can be saved by reusing dye effluents which can largely influence not only the environmental issues but also the cost-effectiveness of dyeing industries.
Keywords: Color Fastness; Cost-effectiveness; Dye Effluents; Environment; Reuse; Shade Difference
© 2020 Karim, Islam, Dutta, Hossain, Bain. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.