

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 25, Pages: 2520-2528
Original Article
Mohamad Ahmad Saleem Khasawneh1*
1Special Education Department, King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:02 April 2020, Accepted Date:28 April 2020, Published Date:17 July 2020
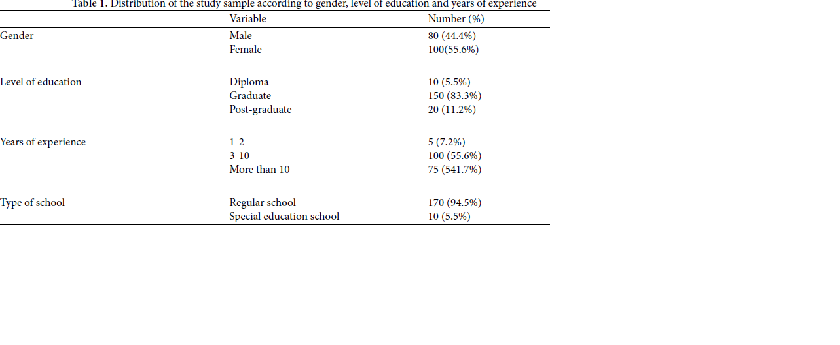
Objectives: To examine the leadership roles of Saudi special education teachers from their own perspective and to survey their views toward challenges in leadership. Methodology: The study used the survey method, for which a questionnaire was developed and distributed to a sample of (n = 200). The results indicated that special education teachers had little experience in leadership roles, where they considered participation in conflict resolution among colleagues as their most important leadership role participation in mentoring, follow-up or training is the least important. Findings: The results of the study revealed that there were no statistically significant differences between male and female special education teachers in their level of enacted leadership. The level of education and years of experience were found to have a significant impact on the leadership level of teachers. Novelty of the study: the inclusion of students with special needs in regular schools require teachers with leadership skills. Therefore, this study came as the first study to tackle this topic in Saudi Arabia.
Keywords: Leadership; special education teacher; perceptions; educational reform
© 2020 Khasawneh.This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.