

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2021, Volume: 14, Issue: 30, Pages: 2472-2482
Original Article
Ashutosh Shukla1*, Ajey Kumar Vishwakarma2, Hiroko ONO3, Mustafa Said Habibi4
1M. Eng, Civil Engineering and Architecture, University of the Ryukyus, Okinawa, Japan
2B. Tech, Civil Engineering, Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology, Gorakhpur,
Uttar Pradesh, India
3Professor, Civil Engineering and Architecture, University of Ryukyus, Okinawa, Japan
4Doctoral Student, Civil Engineering and Architecture, University of Ryukyus, Okinawa, Japan
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:09 March 2021, Accepted Date:24 June 2021, Published Date:13 September 2021
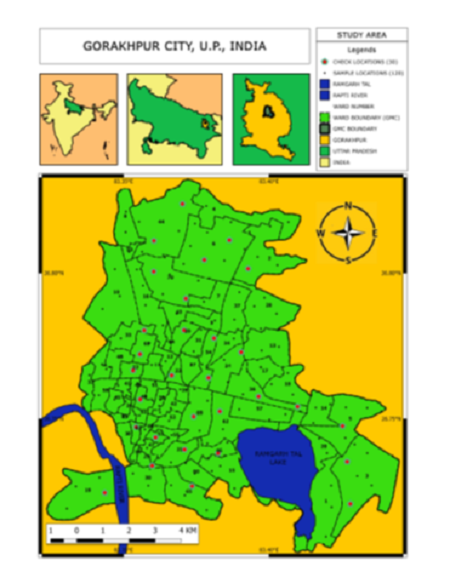
Objective: This study involves application of Geographic Information System (GIS) technique for assessment of the groundwater quality using the features and working of the GIS software for plotting the geospatial data which is very useful in monitoring the groundwater quality for effective management. The groundwater quality in the Gorakhpur district has special significance and needs great attention of all concerned because it is the only source of water for industrial, domestic and irrigation water supply. Method: The groundwater samples were collected manually from the available water sources from 150 locations distributed in Gorakhpur city. Quantum GIS was used for WQI & spatial-distribution data maps of 150 Samples. WQI and weighted overlay maps were produced, which provide a better understanding of the existing water Quality Scenario of Gorakhpur City. WQI classifies water into five categories that are Excellent, Good, Poor, Very Poor & Water unsuitable for drinking purposes. The weighted overlay maps were created in the study area from the spatial distribution of seven water quality parameters. Finding: Quality analysis of the drinking water such as spatial distribution maps of individual water quality parameters, Water Quality Index was found and various stress zones in Gorakhpur City were identified. According to WQI, out of 150 samples, only 3 samples were found of Poor Ground Water for drinking purposes sampled inwards Purdilpur (Ward 42), Dilejakpur (Ward 38) and Alhadadpur (Ward 55) with WQI of 103.54, 100.17 and 100.11, respectively. The best water sample is that whose WQI is the least. Shaktinagar (Ward 37) was found to have the best results with a WQI of 59.05 i.e., good water. None of the samples were found as ‘Excellent’. Novelty: This study proposed a concept of assessment and categorization of the groundwater quality based on WQI, which took 7 parameters into consideration so that proper steps of monitoring, and management can be done to stop the deterioration of the quality of water.
Keywords: Ground water; Water Quality Index (WQI); Weighted Overlay; GIS; IDW Surface Interpolation; Spatial Distribution
© 2021 Shukla et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.