

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v16i45.1669
Year: 2023, Volume: 16, Issue: 45, Pages: 4233-4243
Original Article
K Bindu Kumar1, K R Remesh Babu2*, Ramesh Unnikrishnan3, U Sangeetha4
1Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Government Engineering College, Barton Hill, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India
2Professor, Department of Information Technology, Government Engineering College,
Painavu, Idukki, Kerala, India
3Associate Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Engineering Munnar, Kerala, India
4Associate Professor, Department of Information Technology, Government Engineering College, Sreekrishnapuram, Palakkad, Kerala, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:06 July 2023, Accepted Date:31 October 2023, Published Date:06 December 2023
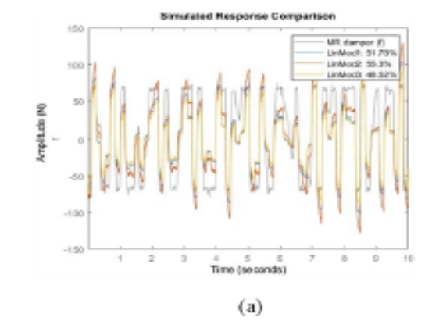
Objectives: Despite significant advancements in the field of automotive suspension systems, a notable research gap exists in accurately predicting the intricate nonlinear damping behavior of Magnetorheological Dampers (MRDs), which hinders the comprehensive enhancement of automotive comfort and safety. This study aims to address this gap by developing a novel machine learning-based black box model capable of precisely forecasting the complex damping characteristics exhibited by MRDs, thereby paving the way for substantial improvements in both ride comfort and vehicle safety. Methods: A methodology integrating machine learning and real-time feedback control is employed, utilizing Linear, Nonlinear Autoregressive with Exogenous Variables (ARX), and Hammerstein-Wiener models for input selection and parameter estimation. Experimental data from hydraulic testing is used to develop a nonlinear black box model using a NARX structure. Inputs of MRD force and velocity predict the corresponding damping force, improving stability and generality compared to physical modeling methods. Findings: The successful implementation of the proposed methodology enables the identification of a model that closely matches experimental data obtained from an MR damper. The developed non-linear black box model, combined with constructive parameter estimation models, improves the understanding and control of MR damping behaviour. Novelty: This advancement contributes to the field's progress by offering a novel approach for predicting the damping behaviour of MRDs, facilitating their effective utilization in various applications across the automotive and other industries.
Keywords: Magnetorheological fluids, Nonlinear dynamics, Feedback control, Machine learning, MR damper, Dynamic modeling
© 2023 Kumar et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.