

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2021, Volume: 14, Issue: 37, Pages: 2880-2887
Original Article
Yvette D Medrano1*, Gerald M Duza1, Ricardo B Casauay1, Andrea F Dawan1, Lyle Gavien L Alcomendras2
1Faculty, College of Agriculture, Cagayan State University-Piat Campus, Baung Piat Cagayan R02, 3527, Philippines
2Research Assistant, College of Agriculture, Cagayan State University-Piat Campus, Baung Piat Cagayan R02, 3527, Philippines
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:03 April 2021, Accepted Date:28 September 2021, Published Date:09 November 2021
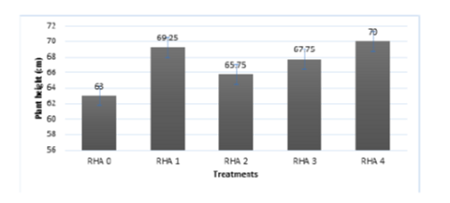
Objectives: Silica is not essential nutrients for plant growth; however, it shows that it is beneficial to rice, especially under stress conditions. This study is to test the efficacy of Rice Hull Ash (RHA) as a silicon source to enhance rice resistance against bacterial leaf blight, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Methods: The Complete Randomized Design (CRD) was adopted for the different treatments, replicated four (4) times. CSUT0 (control), CSUT1(30 grams RHA, Basal Application), CSUT2(30 grams RHA, Basal Application; 15 DAT), CSUT3 (30 grams RHA, Basal Application; 15 DAT and 30 DAT), and CSUT4 (30 grams RHA, Basal Application, 15 DAT, 30 DAT; and 40 DAT). The effect of all the treatments is on the severity of infection of the bacteria, plant height and wt.% of SiO2 acquired from soil, RHA and test plant. Findings: Rice Hull Ash (RHA) composed of 87.34 wt. % of SiO2 while soil collected from the Rice Field composed of 68.49 wt.% of SiO2, Disease resistance is as high as 60% when compared with the highest infection rate (T0) to the lowest infection rate (T4). Plant height and resistance produced against BLB infection was observed significantly in CSUT3 (Basal application at 15 and 30 DAT and 30 grams of RHA). Novelty: The study offers an interesting organic alternative that could be used in controlling Bacterial Leaf Blight (BLB).
Keywords: Bacterial Leaf Blight; Rice; Rice hull ash (RHA); Resistance Mechanism; Silica (SiO2)
© 2021 Medrano et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.