

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v16i10.2119
Year: 2023, Volume: 16, Issue: 10, Pages: 680-697
Original Article
Irshad Ahmad Thukroo1, Rumaan Bashir2*, J Kaiser Giri2
1Research Scholar, Department of Computer Science Islamic University of Science & Technology, Kashmir
2Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science Islamic University of Science & Technology, Kashmir
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:02 November 2022, Accepted Date:09 December 2022, Published Date:07 March 2023
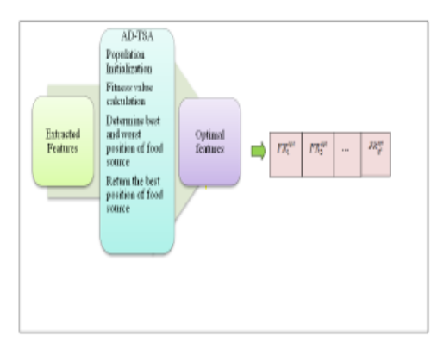
Objective: Spoken language identification being the fore-front of language recognition tasks and most significant medium of communication has to be enhanced in order to improve the accuracy of recently developed spoken language recognition systems. The purpose of this paper is to enhance the Spoken Language Identification (SLID) model using hybrid machine learning with deep learning model for regionally spoken languages of Jammu & Kashmir (JK) and Ladakh. Method: Initially, the speech signals of different languages of JK and Ladakh are manually collected from diverse sources, and it is preprocessed using Spectral Noise Gate (SNG) filtering technique. Once the speech signals are pre-processed, the feature extraction is performed by the cepstral features like Mel-frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs), Relative Spectral Transform-Perceptual Linear Prediction (RASTA-PLP), and spectral features like spectral roll off, spectral flatness. Findings: From this feature extraction, the length of the feature vector seems to be long, and it is required to reduce the feature length. Hence, optimal feature selection is accomplished using the new meta-heuristic algorithm termed Adaptive Distance-based Tunicate Swarm Algorithm (AD-TSA) by considering the minimum correlation as objective. Finally, the language identification is handled by the hybrid classifier termed Improved Support Vector Machine-Recurrent Neural Network (ISVM-RNN). Novelty: The identification learning algorithm is enhanced by the AD-TSA by considering the minimum correlation as objective among features in order to get minimum number of features that are sufficient for language identification process. The efficiency of the proposed hybrid approach is validated by simulating the experiment on a user-defined language database of JK and Ladakh speech signals in the working platform of Python.
Keywords: Language Identification; Kashmir Languages; Optimal Feature Selection; Improved Support Vector MachineRecurrent Neural Network; Adaptive DistanceBased Tunicate Swarm Algorithm
© 2023 Thukroo et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.