

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2022, Volume: 15, Issue: 36, Pages: 1769-1778
Original Article
B Pushpa1*, V Narmatha1, P Anandababu1, C Senthilkumar1
1Assistant Professor, Department of Computer and Information Science, Annamalai University
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:18 June 2022, Accepted Date:19 August 2022, Published Date:21 September 2022
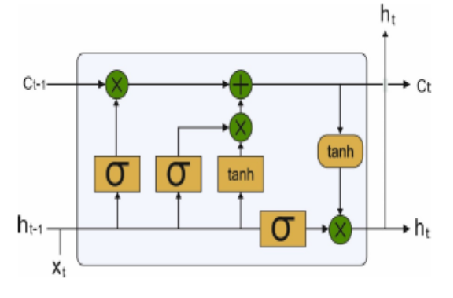
Background: In the present digital era, fraud detection using surveillance video has become a mandatory tool to determine the occurrence of abnormal events in an automated way. Since the traditional visual inspection of surveillance videos for fraud detection is time-consuming and labour-intensive, intelligent fraud detection approaches based on Deep Learning (DL) concepts have been presented in the literature. Methods: This paper designs a DL with optimal classification based on fraud detection in a video surveillance system, named the DLOC-FDVS technique. The proposed DLOC-FDVS technique aims to examine the surveillance videos for the existence of frauds (i.e., robbery) in the IoT environment. At the initial stage, IoT enables the data acquisition and frame conversion process to be carried out. For fraud detection, densely connected networks (DenseNet-169) feature extractor and optimal Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) classifiers are applied. Finally, the Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm (GOA) is utilised to alter the LSTM model’s hyperparameters. It is frequently employed in a number of industrial settings and achieves suitable answers due to its ease of deployment and excellent precision. Findings: The DLOC-FDVS model is experimentally validated using a benchmark anomaly detection dataset from the Kaggle repository, which comprises 211 frames of normal video and 100 frames of fraud video. The experimental results show that the suggested model is an excellent fraud detection tool in the IoT context, achieving maximum precision, recall, F1score, and AUC of 96.56%, 96.56%, 96.56%, and 96.56% respectively. Novelty: The use of GOA for hyperparameter adjustment of the LSTM model for fraud detection demonstrates the work’s uniqueness. As a result, the DLOC-FDVS model may be used to identify fraud in real-time surveillance recordings.
Keywords: Video surveillance; Deep learning; Video processing; Internet of Things; Fraud detection; Hyperparameter tuning
© 2022 Pushpa et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.