

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v16i44.2280
Year: 2023, Volume: 16, Issue: 44, Pages: 3995-4001
Original Article
Mamta Chauhan1*, Swati Gupta2
1Professor, IIHMR University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
2Senior Specialist, Obstetrics and gynaecology, Department of Medical and Health Services, Rajasthan, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:07 September 2023, Accepted Date:06 October 2023, Published Date:21 November 2023
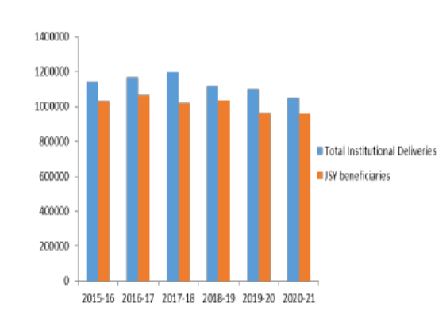
Objectives: Maternal health indicators not only reflect women's well-being but also serve as critical indicators of overall societal health and socio-economic development. Therefore, improving maternal and child health has been a priority across countries. In India, particularly in the State of Rajasthan various programs and initiatives have been implemented to improve maternal health. The objective of this article is to understand the impact of these programs and initiatives on maternal mortality rates, maternal healthcare utilization, and the overall well-being of women. This evaluation is important to measure the effectiveness of these initiatives and also for guiding future policies and interventions aimed at further enhancing maternal health. Methods: A comprehensive descriptive analysis of maternal health in Rajasthan was conducted through a review of government program utilization and implementation data. Secondary data on literacy rates, ANC registrations, institutional deliveries, maternal deaths, and maternal death audits from various sources, including government reports and surveys was reviewed by study team. The analysis focused on trends and changes observed during the period from 2011 to 2021 and identifying the gaps for suggesting recommendations for further improvement in Maternal health. Findings: According to our analysis, Rajasthan has made significant progress in maternal healthcare. The maternal mortality ratio (MMR) decreased from 244 in 2011–13 to 141 in 2017–19, indicating improved healthcare accessibility. Over time, programs like Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) and Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram (JSSK) have led to a reduction in maternal and child healthcare costs, benefiting a broader spectrum of individuals. The Kushal Mangal Karyakram and Safe Motherhood Day camps successfully identify and assist in high-risk pregnancy situations. However, to achieve sustainable development goals, it's crucial to address the gaps in maternal care. Maternal death audits are essential tools for this purpose, but the data revealed that less than 50% of maternal deaths are being reported, and among the reported cases, the reported data is incomplete. Conclusion: Hence accurate and routine information on causes of maternal deaths is very important for implementation of interventions and tracking and interpretation of the gaps in coverage for improving maternal health in Rajasthan.
Keywords: Maternal Health, Rajasthan, Government Programs, Janani Suraksha Yojana, Maternal Mortality
© 2023 Chauhan & Gupta. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.