

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 12, Pages: 1347-1354
Original Article
G C Sowparnika1*, M Thirumarimurugan2, N Vinoth3
1Assistant Professor, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Sri Shakthi Institute of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore, 641062, Tamilnadu, India. Tel.: +91-91585948433
2Professor & Head, Department of Chemical Engineering, Coimbatore Institute of Technology, Coimbatore, 641014, Tamil Nadu, India
3Assistant Professor, Department of Instrumentation Engineering, Madras Institute of Technology, Chennai, 600044, Tamil Nadu, India
*Author for correspondence
G C Sowparnika
Assistant Professor, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Sri Shakthi Institute of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore, 641062, Tamil Nadu, India.
Tel.: +91-91585948433
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:31 March 2020, Accepted Date:23 April 2020, Published Date:08 May 2020
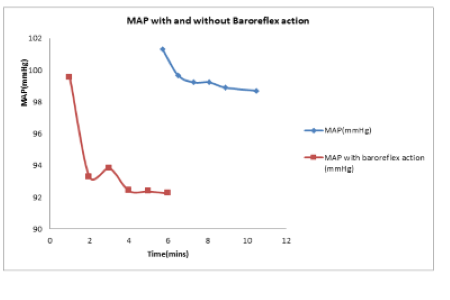
Background: Manual drug infusion during surgeries is inaccurate and timeconsuming which has been adopted technique in most of the hospitals. Methods: Based on clinical data, it is evident that the manual control is inaccurate and takes prolonged time to bring into effect, if any change in infusion rate is required during clinical practice. Considering this drawback, the modeling of cardiovascular system (CVS) and baroreceptor (BR) is developed using miscellaneous differential equations based on compartmental approach. The control variables are mean arterial pressure (MAP) and cardiac output (CO) obtained from CVS-BR model. Findings: The manipulated variables are noradrenaline (NAR) and nitroglycerine (NG) infusion rate which is modeled using the relationship between volume and drug mass effect equations on CVS-BR model. For the open loop transfer function derived from the model, relative gain array (RGA) analysis is performed to identify the influence of maximum effect of manipulated variables on the physiological parameters. The simulation results obtained from MATLAB are correlated using time domain specifications and error criteria. The performance index reveals the least error and facilitates in accurate infusion of drugs to the patient during cardiovascular surgeries. Novelty: The automatic controller during surgery provides safe operating condition and speedy recovery of the patients and also helps the anaesthetist to monitor and regulate the physiological variables.
Keywords: Control strategy; Error criteria; Drug infusion; Modeling; Relative gain array; Simulation
Copyright: © 2020 Sowparnika, Thirumarimurugan, Vinoth. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.