

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 16, Pages: 1668-1675
Original Article
Mehjabin Z Shaikh1∗
1 Consultant-Environment, Gujarat Industrial & Technical Consultancy Organization Ltd, 380 009, Ahmedabad, India. Tel: 9638196608
∗Corresponding author:
Mehjabin Z Shaikh
Consultant-Environment, Gujarat Industrial & Technical Consultancy Organization Ltd, 380 009, Ahmedabad, India.
Tel: 9638196608
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:13 April 2020, Accepted Date:08 May 2020, Published Date:09 June 2020
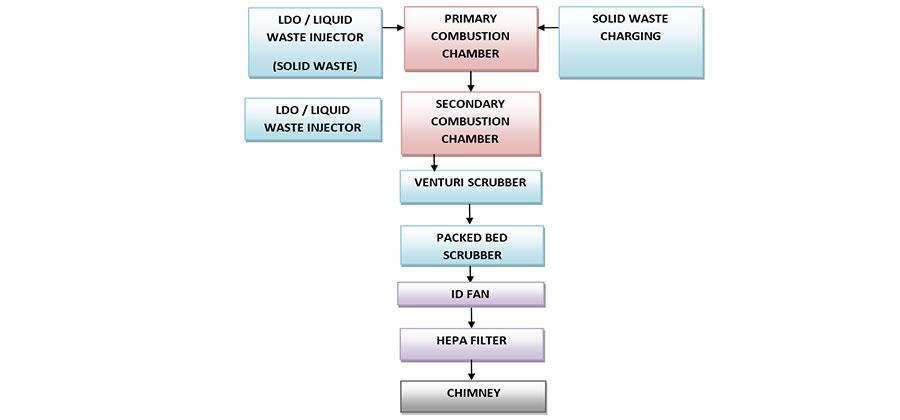
Background/Objectives: Hazardous waste incineration is one of the proven technologies for complete destruction of hazardous wastes. These facilities, when designed and operated properly are capable of destroying the hazardous organic components in waste along with PCBs. If these facilities are designed and not operated efficiently, could act as a significant source of such hazardous substances to the environment. Common hazardous waste incineration facilities are designed based on assumptions regarding the availability of quantity and quality (characteristics) of waste. The actual operating waste recipe and performance may differ considerably than the designed. So performance evaluation on actual operating data becomes necessary to check the operational efficiencies and levels of pollutants emitted into the environment. This implies the need for system analysis and solutions by independent assessment procedure. This study focused on the baseline performance evaluation of common hazardous waste incineration facility based on actual plant operating data located in India for Ship Scraping Waste. Methods: Inspection, monitoring and analysis were carried out to characterize all feed and effluent stream. Heat and mass balance were developed and actual operating efficiencies were evaluated. Findings: The results show that temperature and detention time achieved in the secondary chamber were 1150◦ C and 2.6 sec respectively, which are above the statutory requirement of 1100 + 50 and 2 seconds. The LOI in Ash was 2.5 %. The flue gas composition indicates 6.12 % Oxygen and 10.20% Carbon Dioxide levels, a good combustion efficiency and ensures sufficient amount of air needed for complete combustion. Flue gas analysis indicates PM, SO2, NOx, HCl levels were well below permissible limits and absence of Dioxins and Furans. Destruction efficiency achieved for PM and HCl are 99.53% and 95.62 % respectively to meet the statutory norms. Novelty : Thus, from the study and analysis of results, it is inferred that the common HW Incinerator in the study is operated systematically and efficiently on actual plant operating conditions and meeting all the requirements of Central Pollution control board of India. The research findings will act as benchmarking for optimal plant operational practices for quality of incineration for ship scraping waste.
Keywords: Incinerator; Hazardous Waste; Mass and Heat Balance; Destruction Removal Efficiencies
© 2020 Shaikh. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.