

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2022, Volume: 15, Issue: 9, Pages: 395-407
Original Article
Samuel Duraivel1*, R Lavanya2
1Ph.D, Research Scholar, Department of Media Sciences, CEG Anna University, 600 025, Chennai
2Assistant Professor, Department of Media Sciences, CEG Anna University, 600025, Chennai
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:21 September 2021, Accepted Date:03 November 2021, Published Date:07 March 2022
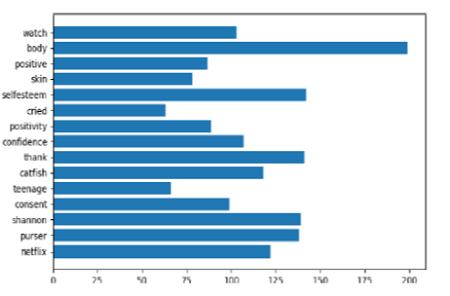
Objectives: [a] To understand how popular millennial media usage practices can be used to improve self-esteem among the millennial cohort; [b] To ascertain the effect of VoD and OTT streaming services in improving levels of self-esteem. Methods: Natural Language Processing techniques, namely, Term Frequency analysis, Network analysis, and Opinion Mining were used to identify and analyze the user generated Twitter Corpus dataset. Using Tweepy, a Python module, the data (n = 2566 tweets) were retrieved from the RESTAPI (Application Programming Interface) of Twitter. NLTK (Natural Language Processing ToolKit), NetworkX, and TextBlob were used for Opinion mining and visualization of the datasets Findings: Binge-watching of VoD and OTT content that address issues related to Body Positivity and Self-esteem resulted in improvement among the viewer cohort. Analysis of the Twitter corpus dataset implied that the following latent factors contributed toward the observed outcome: relatability (23:14%), upliftment(19.4%), gratitude(36.11%), and relief (21.2%). Novelty: Application of Natural Language Processing to identify latent factors that contribute toward either positive or negative outcome(s) has not been conducted before. Our previous research on similar areas identified latent factors that contribute toward behavioral outcomes in terms of attitude toward vaccines.
Keywords: Selfesteem; Bingewatching; Therapy; Netflix; Behavioral outcomes
© 2022 Duraivel & Lavanya. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.