

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 22, Pages: 2203-2213
Original Article
Akanksha Dwivedi1∗, Vadamalai Elangovan1 , Manisha 1 , Pawan Kumar misra1
1 Department of Zoology, School of life sciences, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar university, Vidya vihar Raibareli road, Lucknow, 226025, Uttar pradesh, India. Tel.: +917985328203
∗Corresponding author:
Akanksha Dwivedi
Department of Zoology, School of life sciences, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar university, Vidya vihar Raibareli road, Lucknow, 226025, Uttar pradesh, India.
Tel.: +917985328203
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:30 May 2020, Accepted Date:28 May 2020, Published Date:24 June 2020
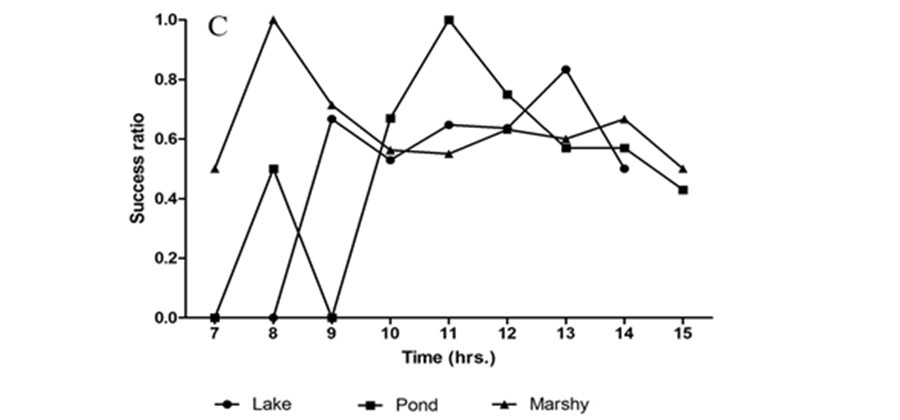
Objectives: The present study was focused on feeding behaviour and foraging success of Indian pond heron (Ardeola grayii) in different seasons and habitats. Methods: The study was carried out in three habitats, lake, pond and marshy area from September 2016 to December 2017. All activities such as feeding behaviour, foraging success, prey abundance, success ratio, feeding frequency (foraging attempt and success) of A. grayii were compared in three habitats with three seasons by using binocular and video recorder. Statistical analysis: Data were analysed by SPSS (21 version) and graph pad prism. In this study, prey abundance and foraging success in three habitats and season differed statistically significant (p < 0.05). By using non-linear regression on foraging attempt and success in three habitats three curve (exponential, cubic, growth and power) best fitted to analyzed data sets. These curve shows variation in feeding pattern. Findings: Stand and wait is dominant feeding behaviour followed by walk slowly and walk quickly in all three habitats and season. Prey was abundantly present during monsoon, as a result feeding frequency and success ratio maximized. Structure of habitats, vegetation, and water depth also influenced foraging success of Ardeola grayii. Thus, overall finding showed that Indian pond heron feeding behaviour and foraging success affected by structure of habitats and seasons.
Keywords: Habitat; season; feeding; frequency; behaviour; prey
© 2020 Dwivedi, Elangovan, , misra. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.