

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v17i10.2811
Year: 2024, Volume: 17, Issue: 10, Pages: 932-940
Original Article
Rahul P Neve1*, Rajesh Bansode2
1Research Scholar, Department of Information Technology, Thakur College of Engineering and Technology, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
2Professor, Department of Information Technology, Thakur College of Engineering and Technology, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:06 November 2023, Accepted Date:12 February 2024, Published Date:27 February 2024
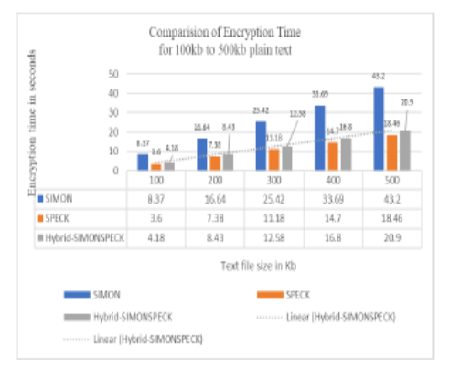
Objective: To perform attack analysis on new developed hybrid-SIMON-SPECKey lightweight cryptographic algorithms and compare its strength with existing SIMON and SPECK Lightweight cryptographic algorithm. Methods: A hybrid-SIMON-SPECKey algorithm is the combination of round function of SIMON and key scheduling of SPECK algorithm. Both SIOMN & SPECK algorithm are used for securing resource constrained devices. In this research work, avalanche effect method is used to analyze attack resistance property of algorithm. Findings: Newly developed Hybrid algorithm shows better results in terms of execution time and memory consumption. As compared to SIMON, hybrid version of algorithm consumes 50% less time and 20% less memory, which makes it efficient. Strict Avalanche criteria for SIMON is 89%, that of SPECK is 90% and in case of hybrid algorithm, it is 90% at start position but when the character is flipped or changed at the end position of plain text then SAC is more (87%) in case of hybrid algorithm as compared as SIMON and SPECK algorithms. Hence, newly developed algorithm showed improved results with equally resistance to the attack as compared to SIMON & SPECK. Novelty and applications: The novelty lies in the creation of a hybrid lightweight cryptographic algorithm that combines the feistel structure of SIMON with the key scheduling function of SPECK. This hybrid approach aims to leverage the strengths of both algorithms, potentially providing a more robust and efficient solution for resource-constrained IoT devices. In section 3.1 comparative analysis is done which show that hybrid algorithm outperforms in term of time and memory consumption as well a strength of newly developed hybrid algorithm is evaluated using avalanche effect which shows that it is at par with base algorithms.
Keywords: Attack Analysis, Cipher Code, Decryption, Encryption, Lightweight Cryptography, Iot Devices, And Resource Constraint Devices
© 2024 Neve & Bansode. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.