

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v13i11.149583_2020
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 11, Pages: 1243-1247
Original Article
Ranjeet Kumar1, Mehtab A Mahar1, Sadaf Jumani1, Rashida Bhanbro1, Faiza Qazi1, Mazhar Ibupoto1, Fozia Soomro1, Khadim H Memon1∗
1Department of Zoology, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Shah Abdul Latif University, Khairpur, Sindh, Pakistan
*Author for correspondence
Khadim H Memon
Department of Zoology, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Shah Abdul Latif University, Khairpur, Sindh, Pakistan.
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:03 February 2020, Accepted Date:19 March 2020, Published Date:21 March 2020
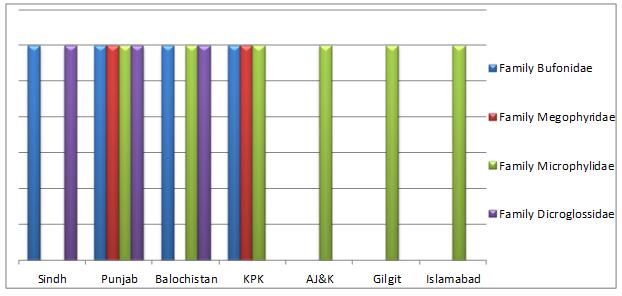
Objectives: The present study was conducted to review the biodiversity of Amphibians, their decline in population and conservation. Methods/Statistical analysis: This study was done by reviewing the previous papers on biodiversity of Amphibians and available literature on various search engines. Findings: Species of amphibians estimated worldwide reveals 7481 species consisting of three orders, Salientia (Anura), Urodela (Caudata) and Apoda (Gymnophiona). The Salientia contains 6577, Urodela (Caudata) entail 698 species of both land and aquatic inhabitants and Apoda (Gymnophiona) virtually blind and nonmotile animals include 206 species. However, the population of Amphibians is reduced in Pakistan because of dry conditions and is a prominent indicator of climatic change. In Pakistan, the dominating population of Amphibians is Salientia (Anura), consisting of 21 species, 12 genera, and 4 families. Due to anthropogenic activities like the use of pesticides and fertilizers, deforestation, pollution, fragmentation and urbanization affects the amphibians. For conservation and protection, serious initiatives may be mediated to manage the situation. Application/Improvements: The present study will be helpful to conserve the diversity of Amphibians in the region and present findings may be useful in future studies.
Keywords: Amphibia; Pakistan; Decline; conservation; Population
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.