

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2024, Volume: 17, Issue: 27, Pages: 2820-2828
Original Article
Sarah Tarek Ghaly1∗, M F Abadir1, M A Sorour2, F I Barakat1
1The Chemical Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt
2Food Technology Research Center, Egypt
*Corresponding Author
email: [email protected]
Received Date:03 January 2024, Accepted Date:01 June 2024, Published Date:13 July 2024
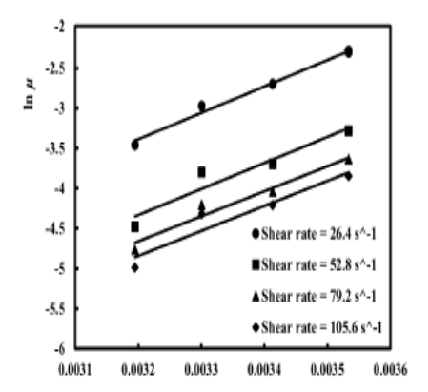
Objective: A water treatment facility is to be erected nearby the industrial tanning complex, recently established East of Cairo, Egypt. This paper represents a contribution to studying the flow characteristics of the produced tannery waste effluents. A dried sample of tannery waste was chemically analyzed by X-ray fluorescence and its particle size distribution was determined. Next, rheological measurements were carried out on the waste slurry produced at temperatures ranging from 10°C to 40°C and three different solid concentrations, by weight: 20%, 25%, and 30%. The results showed that all waste suspensions under all conditions of solid content and temperature behaved as shear-thinning liquids. Flow indices of all suspensions generally tended to increase with temperature and solid concentration. Activation energies for viscosity were correlated to an increase in solid concentration and showed a decreasing pattern. All samples exhibited a thixotropic character that decreased with increased temperature and dilution of the suspension. The maximum pressure drops per unit length of a pipeline used to transport the waste suspension to the treatment unit was evaluated and found to increase with solid concentration and decrease with increasing temperature.
Keywords: Rheology, Tannery waste slurry, Solid content, Temperature
© 2024 Ghaly et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.