

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 19, Pages: 1901-1907
Original Article
Anita Jessie J1 , Peerzada Danish1,2∗, S Ganesh3 , Chandandeep Singh Raina4
1 Ph.D. Research Scholar, School of Civil Engineering, Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, 632014, Tamil Nadu, India
2 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Model Institute of Engineering and Technology, Jammu, 181122, Jammu and Kashmir, India
3 Assistant Professor, School of Civil Engineering, Lovely Professional University, Jalandhar, 144411, India
4 Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, GGS College of Modern Technology, Mohali, 140104, Punjab, India
∗Corresponding author
Peerzada Danish
Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Model Institute of Engineering and Technology, Jammu, 181122, Jammu and Kashmir, India
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:12 May 2020, Accepted Date:19 May 2020, Published Date:18 June 2020
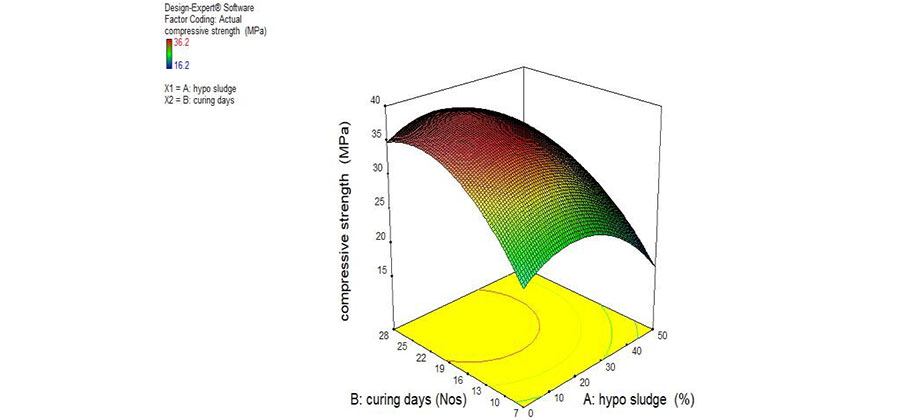
Objectives: The objective of the study was to study the compressive strength of the partially replaced paper mill waste in cement. Methods/ Statistical analysis: The concrete cube specimen were prepared for compressive strength test. In this study, the cement has been replaced with 20%, 30%, 40% and 50% of hypo sludge. The specimens were cured for two different ages (7 days and 28 days) and tested for compressive strength. The quadratic polynomial prediction equation was proposed using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). The prediction model was developed using the experimental output results. Thus, the prediction model facilitates the further research work to be conducted by researchers on paper mill waste replacement. The rate analysis was also further carried out to show the cost effectiveness of using the waste replacement in cement. Findings: The test was conducted on the compressive strength (7 days and 28 days) of control specimen (0%) and partial replacement of 20%, 30%, 40% and 50% of cement using the hypo sludge. Thus, 20% replacement of cement using hypo sludge has shown good compressive strength than the control specimen. The cost of 20% paper mill waste was less when compared to the cost of control specimen. Novelty/ Applications: The compressive strength of 20% partial replacement of paper mill waste in cement can be used in further construction. The prediction model can be used to predict the future compressive strength of partially replaced paper mill waste concrete.
Keywords: Ordinary Portland cement; Paper mill waste; Hypo sludge; Partial replacement; RSM
© 2020 J, Danish, Ganesh, Raina. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.