

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2021, Volume: 14, Issue: 2, Pages: 181-189
Original Article
Sushil Kumar1, Praveen Bhatt2,3*
1Research Scholar, Department of Physics, Banasthali Vidyapith, Banasthali, Rajasthan, India
2Adjunct Faculty, Banasthali Vidyapith, Banasthali, Rajasthan, India
3Professor, APIIT SD INDIA, Panipat, Haryana, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:02 November 2020, Accepted Date:26 December 2020, Published Date:21 January 2021
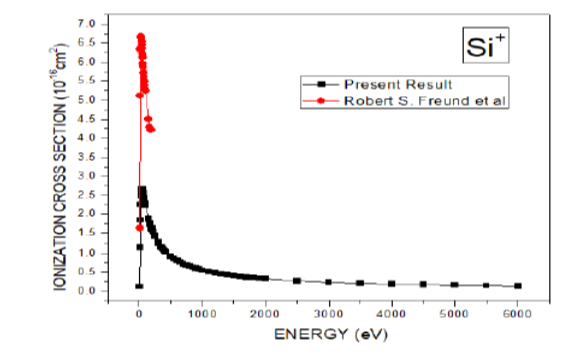
Abstract:Electron-impact single-ionization cross sections of Si by electron impact have been solved theoretically for the full range of kinematics and collision geometries of practical interest by S.P. Khare theoretical model. The corresponding partial and total ionization cross sections have also been derived in the energy range varying from ionization thresholds to 6000 eV. Comparison of the evaluated partial and total ionization cross sections is made with the experimental and theoretical data wherever available. Objective:Our objective is to find the partial and total ionization cross sections Silicon atom and its fragmentation ion at different energy levels and analysis of results with other available data. Method: In this present work we have measured partial ionization cross sections of Silicon atom using semi-empirical formalism of Jain & Khare due to electron impact at incident electron energy from ionization threshold to 6000 eV. Findings: Comparison of the evaluated partial and total ionization cross sections is made with the experimental and theoretical data wherever available. A good agreement is observed when we compared our data for electron impact ionization cross section for Silicon and its fragment ions. Also some disagreement is found between our data and other available data. Our results are higher for Si2+, Si4+, Si5+ and Si6+ fragment ions. For Silicon atom, good agreement between theory and experiment is achieved. Novelty: The total ionization cross-sections by electron impact of atoms are required in the study of plasma diagnostics, astrophysical and fusion applications, radiation physics, mass spectrometry, ionization in gas discharge, modeling of fusion plasmas, modeling of radiation effects for both materials & medical research and astronomy. We have calculated partial and total ionization cross section for higher energy range i.e from threshold to 6000 eV, which have not been done by other researchers.
Keywords: Ionization; cross section; electron impact
© 2021 Kumar & Bhatt.This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.