

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v17i22.1041
Year: 2024, Volume: 17, Issue: 22, Pages: 2316-2323
Original Article
E Punithavathy1*, N Priya2
1Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Applications, Madras Christian College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
2Associate Professor, PG Department of Computer Science, Shrimathi Devkunvar Nanalal Bhatt Vaishnav College for Women, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:01 April 2024, Accepted Date:20 May 2024, Published Date:30 May 2024
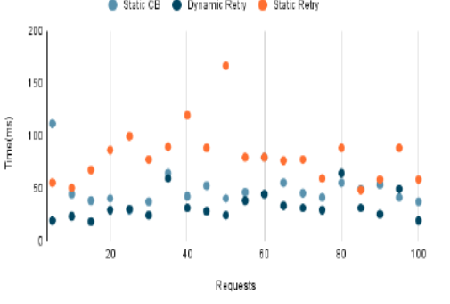
Objectives: The main objective of this study is to enhance the flexibility of microservice-based cloud applications, so they can cope with transient or short-term failure conditions more effectively, providing a higher throughput of cloud applications as a result. Methods: The comparison is done between the existing or manual resilient patterns such as circuit breaker and retry with a dynamically proposed retry patterns using a microservice application. Findings: The short-term or transient failures in cloud based microservice applications can occur for many reasons. Examples such as Network glitches, service failures, timeouts of requests etc. These failures can bring down the entire application resulting in a cascading of failures. Resiliency patterns are used to protect these applications from failures. The widely used patterns are circuit breaker and retry, with static configurations. It is possible that the static configurations used in resiliency patterns might not support all types of failures. Hence, a dynamic approach has been proposed to satisfy all these transient failures of cloud. The analysis proves that the application efficiency is balanced in dynamic retry than the static configurations of resiliency pattern. Hence, performance can be increased up to 34.3%, which means the availability can be ensured, in transient failure cases. Very little research has been carried out on this resiliency pattern, and there are no standards available for this pattern. When comparing with the existing adaptive retry pattern the performance is increased up to 88.52%, while using a microservice application. Novelty: A dynamically modified resilient pattern is been proposed by incorporating additional parameters such as execution time to the existing parameters of the static retry pattern. This is an individual resilience pattern, which can perform independently when compared with other dynamic resilience patterns.
Keywords: Dynamic retry, Request time, Static circuit breaker, Resilience, Static retry
© 2024 Punithavathy & Priya. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.