

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v14i21.2235
Year: 2021, Volume: 14, Issue: 21, Pages: 1791-1805
Original Article
Hidayatullah Kakar 1 , Mehrunisa Memon✉ 1 , Inayatullah Rajpar 1 , Qamaruddin Chachar 2
Received Date:13 December 2020, Accepted Date:27 January 2021, Published Date:19 June 2021
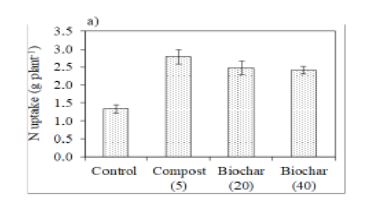
Background/objectives: Biochar has gained tremendous potential for mitigation of climate change and improving soil quality and productivity. This study aimed to develop biochar from banana leaves and evaluate its effect on soil properties and maize yield. Methods: Banana leaf-based biochar, prepared through slow pyrolysis (300-400 oC), was tested on maize crop in pot experiment using three biochar rates (B0 = 0 t ha-1, B1 = 20 t ha-1 and B2 = 40 t ha-1) along with a compost control (Bc = 5 t compost ha-1) and three chemical fertilizer (CF) rates (F0 = 0–Control, F1 = 120 kg N ha-1 and F2 = 120-90 kg NP ha-1) based on completely randomized design with three replications. Findings: The addition of banana leaf based amendments (BLBA) significantly improved soil properties except soil pH and EC. The application of higher biochar rate (40 t ha-1) revealed maximum soil CEC (23.65 cmolc kg-1), TOC (1.48%), TN (0.12%) and K (89.31 mg kg-1) while maximum P concentration (4.26 and 4.04 mg kg-1) was noted in NP and compost applied treatments. Likewise, higher biological (231.00 g pot-1) and grain yield (104.81 g pot-1) as noted in compost treatment, were at par with biochar rates of 20 and 40 t ha-1 which were due to improvement in nutrient uptake. Overall, higher rate of biochar (40 t ha-1) performed better over lower rate (20 t ha-1) and compost (5 t ha-1) in buildup of nutrients and improvement in soil properties. Applications/improvements: Therefore, lower biochar rate and compost of banana leaf origin with chemical fertilizers can serve as an alternate for maize nutrition and improvement in soil fertility and quality So, it is suggested that BLBA may be tested under long term field experiments on different crops.
Keywords
Banana leaves, biochar, calcareous soil, maize, nutrients, slow pyrolysis, yield
© 2021 Kakar et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.