

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2021, Volume: 14, Issue: 26, Pages: 2215-2222
Original Article
Sanket Devikar1*, Khalid Ansari2, Charuta Waghmare2
1PG Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, Yeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering, India
2Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Yeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:02 June 2021, Accepted Date:12 July 2021, Published Date:31 July 2021
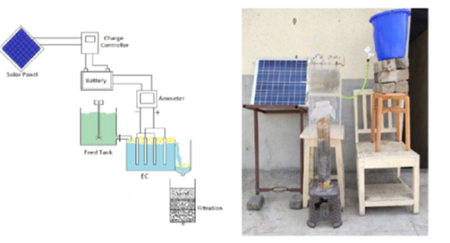
Objectives: To evaluate the importance of solar-based Electrocoagulation followed by the filtration process in treating the domestic greywater, analyze each operational process’s performance process in highlighting the cost, efficiency and reuse conditions. Analysis: This research aimed to see if the continuous mode EC technique could treat Greywater (GW) with batterypowered solar energy. The EC process running on solar energy is used as a single unit method for Greywater treatment. This explores the hybrid electrocoagulation and filtration process with different electrode material combinations with a flow rate; based on this, and the impact tests are carried out on the flexibility of continuous mode, anode and cathode efficiency. Findings: In this experiment, using a combination of electrodes with different material having continuous flow find about removal efficiencies of different characteristics like COD, Total dissolved solids, Total suspended solids, pH and Turbidity with the variable in the supply of current with fix detention time. Novelty:Experimental approach based on Solar based Electrocoagulation with filtration mechanism is the new concept of approach for treating Domestic Greywater
Keywords: Domestic Greywater; Solar energy; Electrocoagulation; Continuous mode; Controlled flowrate; Filtration
© 2021 Devikar et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.