

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v14i48.1148_ii
Year: 2021, Volume: 14, Issue: 48, Pages: 3494-3508
Systematic Review
Natraj Mishra1*, S P SIngh2
1Assistant Professor, School of Engineering, UPES Dehradun, India
2Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Delhi, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:05 July 2021, Accepted Date:19 November 2021, Published Date:28 December 2021
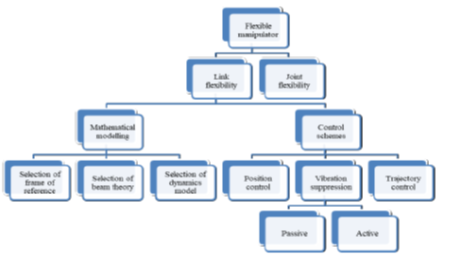
Objectives: This paper addresses two key issues in the area of flexible robotics. The issues are vibration control of flexible links and trajectory control of flexible robots. A brief, yet, significant review is provided that addresses these two issues. Methods: For vibration control of flexible links, possibilities of the use of passive and active damping methods are explored in the literature. After that, the effect of proper trajectory planning to ensure positional accuracy at the end-effector is studied. Findings: After a review of 181 research papers from the year 1970 to 2021, it has been found that the vibration suppression of flexible links can be achieved through the application of viscoelastic materials, piezoelectric materials, and optimum trajectory planning. Recent trends in research in the area of flexible manipulators show that an optimal trajectory can significantly help in reduction of link vibrations and achievement of positional accuracy simultaneously. Novelty: The novelty of the present work lies in exploring the possible application of passive and active damping control methods for vibration suppression of flexible link manipulators. Besides that, the survey also highlights how well planned trajectory may help achieve accurate tip positioning of flexible robots.
Keywords: Flexible manipulator; viscoelastic damping; active vibration control; trajectory planning and control
© 2021 Mishra & SIngh. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.