

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v13i48.1611
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 48, Pages: 4672-4678
Original Article
Jitender Kumar1,2, Vinod Kumar3, Vinay Kumar Singh4*, Upendra Mittal1, Fahim1, Devendra S Barlewar1, A T Nimal1
1Solid State Physics Laboratory, Delhi, India
2Department of Chemistry, Delhi University, Delhi, India
3Special Centre for Nano Sciences, Jawaharlal Nehru University, Delhi, 110067, India
4Department of Chemistry, Sri Aurobindo College, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:07 September 2020, Accepted Date:14 December 2020, Published Date:30 December 2020
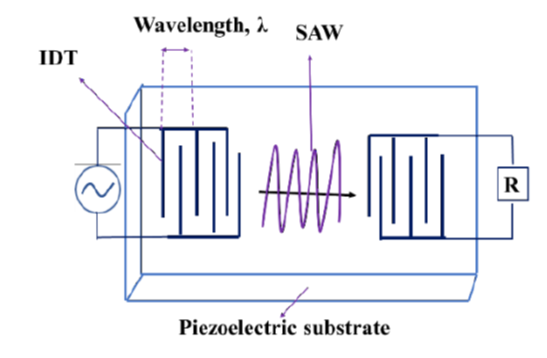
Objectives: To develop gas chromatograph (GC) based chemical agent detector and to compare the response of Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) detector with Flame Ionization Detector (FID) for the development of a reliable and fast gas/vapour analyzer. Also, to describe the limitations of the FID over SAW detector. Methods: An uncoated 433.92 MHz SAW device was used as Gas Chromatography (GC) detector and its response was recorded and compared with conventional FID detector using short capillary column. The response of both the detectors were analyzed by using standard mixture of seven Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). Besides this comparison various key parameter of GC i.e. Flow, temperature and length of GC column were also optimized for fast GC analysis. Findings: After analyzing the fast GC data of both the detectors with same sample, it was observed that the resolution of chromatograms with SAW detector showed more resolved peaks as compare to the FID detector for the same GC parameters. Improvements/Applications: It is concluded that the SAW detector is more suitable for fast and reliable analysis of chemical vapors in rapid analysis.
Keywords: Gas chromatograph detector; surface acoustic wave; volatile organic compounds
© 2020 Kumar et al.This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.