

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2024, Volume: 17, Issue: 2, Pages: 194-203
Original Article
P Balagangatharan1*, R Ramkumar2, P Raja3
1Research scholar (Regd. No. 21211282191006), Department of Zoology, St. Xavier’s College (Autonomous-Affiliated to Manonmaniam Sundaranar University, Abishekapatti, Tirunelveli- 627012, Tamil Nadu), Palayamkottai, 627002, Tamil Nadu, India
2Research scholar (Regd. No. 18211282011024), Department of Zoology, St. Xavier’s College (Autonomous-Affiliated to Manonmaniam Sundaranar University, Abishekapatti, Tirunelveli- 627012, Tamil Nadu), Palayamkottai, 627002, Tamil Nadu, India
3Assistant professor, Department of Zoology, St. Xavier’s College (Autonomous-Affiliated to Manonmaniam Sundaranar University Abishekapatti, Tirunelveli-627012, Tamil Nadu), Palayamkottai, 627002, Tamil Nadu, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:09 November 2023, Accepted Date:16 December 2023, Published Date:12 January 2024
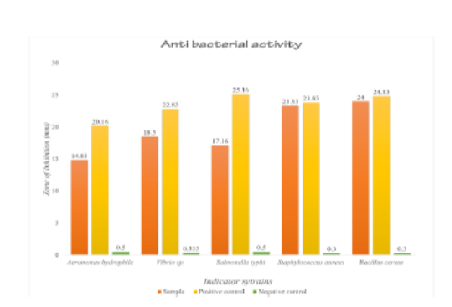
Objective: To isolate and characterize potentially antagonistic bacteria from the gut of Lampito mauritii earthworms. Methods: Lampito mauritii earthworms were collected and gut bacteria were isolated on nutrient agar. Antibacterial activity of isolates was checked by well diffusion against fish and human pathogens. Potent isolates were characterized biochemically. Antimicrobial metabolites were extracted from Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate TR07 using ethyl acetate and tested by disc diffusion. TR07 was identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and phylogenetic analysis. Antibacterial efficacy was assessed statistically. Results: Among 38 discrete isolates, 4 exhibited antibacterial activity against Aeromonas hydrophila and Staphylococcus aureus in well-diffusion assay. These 4 isolates were characterized as Pseudomonas sp., Vibrio sp., Aeromonas sp., and Bacillus sp. based on biochemical tests. Antimicrobial metabolites extracted from Pseudomonas sp. TR07 using ethyl acetate showed statistically significant inhibition against gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial fish and human pathogens in disc diffusion assay. The 16S rRNA gene sequencing and phylogenetic analysis identified the potent isolate TR07 as Pseudomonas aeruginosa with 99.62% sequence homology. Novelty: In a fortuitous finding, the antibacterial potency of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was dramatically amplified through the utilization of a strikingly minute concentration of the bacterial culture extract.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Earthworm gut, Antibacterial metabolites, Human pathogens, Fish pathogens
© 2024 Balagangatharan et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.