

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v16i39.1996
Year: 2023, Volume: 16, Issue: 39, Pages: 3394-3406
Original Article
K Praveen Kumar Rao1*, N Sasikala2, K Shanker3
1Professor & Head, Department of Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning, Kamala Institute of Technology & Science, Singapur, Karimnagar, India
2Professor, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Kamala Institute of Technology & Science, Singapur, Karimnagar, India
3Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Kamala Institute of Technology & Science, Singapur, Karimnagar, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:07 August 2023, Accepted Date:22 September 2023, Published Date:25 October 2023
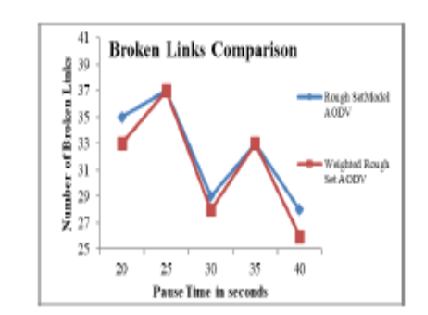
Background/Objectives: A MANET is collection of mobile hosts that often change paths. AODV routing is best for establishing route. There are issues with broadcast storm like contention, collision and interference. They deteriorate performance of QoS. For setting a path, it is necessary to broadcast RRPs, which lead to consumption of bandwidth, congestion and contention. The aim of broadcasting is to decrease flooding. MANETs have limited bandwidth hence necessary to decrease the amount of flooding. Methods: AODV transmits RRPs to adjacent nodes for setting up a route and thus enhances the consumption of network bandwidth. Our approach uses weights assigned to nodes depending on the set of rules framed for determining an appropriate path. The proposal is integrated with AODV with information about 2-hop neighbors. This helps in establishing efficient forward path, thus reducing redundancy. Findings: The limited availability of bandwidth in MANETs, it’s necessary to reduce control packets and considered many parameters for simulation. The outcome of proposed approach is compared with RS-AODV considering conditions like collisions, broken links, energy consumption end-to-end delay and RRPs. Ad hoc networks are found to be constant for a specific period of time and this helps in collecting neighbor node information. This determines an efficient path has been established, thus reducing the packets being broadcasted. Novelty: WRS mechanism is discussed in this paper for reducing the packets being transmitted in the prevailing AODV routing. The simulation exhibits that WRS-AODV approach is 3% energy efficient, throughput achieved with 20.4% enhancement and 65% reduction in the packets being transferred. A mathematical approach for addressing uncertainty and ambiguity, which also takes into consideration the importance of object, is WRS theory. NS-2 used shows to be effective for the proposed model in terms of performance for parameters like throughput, broken links, collisions, end-to-end delay, RRPs and energy consumption.
Keywords: Broadcasting, Flooding, MANET, Weighted Rough Set, AODV, Neighbor Coverage
© 2023 Rao et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.