

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2024, Volume: 17, Issue: 6, Pages: 514-523
Original Article
Suyog C Dharmadhikari1*, Sanjay S Jamkar2
1Resarch Scholar, Applied Mechanics Department, Government College of Engineering, Dr Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, Aurangabad, 431005, Maharashtra, India
2Research Guide, Applied Mechanics Department (Retd), Government College of Engineering, Dr Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, Aurangabad, 431005, Maharashtra, India
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:27 October 2023, Accepted Date:05 January 2024, Published Date:02 February 2024
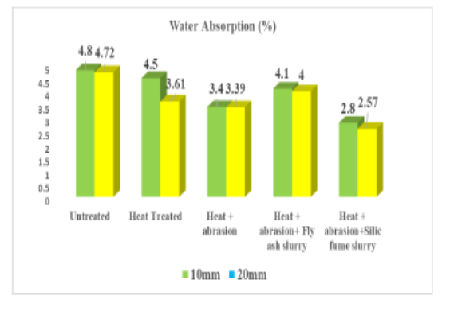
Objectives: This research is aimed at comparing the performance of two sets of treatments. The first set of treatments tests the performance of heated, abrasioned, and fly ash-treated recycled concrete aggregates (RCA), while the other set of treatments examines the performance of heated, abrasioned, and silica fume-treated aggregates. Though previous research has examined the performance of the standalone treatment methods for enhancing RCA properties, there is a research gap that attempts to study the performance of the combinations of various treatments and their merits. To bridge the gap in the literature, this study compares the combination of two sets of treatment methods to investigate the relative effectiveness of the combination of the treatment methods that can improve RCA properties. Methods: The study was conducted using the concrete mix design procedure outlined in IS 10262-2019 in the laboratory. As part of the experimentation program, a total of 24 sample cubes were casted and tested. Findings: A 14.5% reduction in water absorption was observed for 10mm heated, abrasioned, and fly ash-treated aggregates, whereas a 15.2% reduction in water absorption was observed for 20mm heat-treated, abrasioned, and fly ash-treated aggregates compared to untreated aggregates. Similarly, for heat-treated, abrasioned, and silica fume-treated aggregates, a 41.7% reduction in water absorption was observed for 10mm aggregates, and a 45% reduction was observed for 20mm aggregates over untreated aggregates. A 133% increase in slump value was observed for heated, abrasioned, and fly ash-treated aggregates, whereas a 150% increase in slump value was observed in the case of heated, abrasioned, and silica fume-treated aggregates. Further, a 150 % increase in compressive strength was observed for heated, abrasioned, and fly ash-treated aggregates, and a 165% increase in compressive strength was observed for heated, abrasioned, and silica fume-treated aggregates over untreated aggregates. Novelty: This research addresses the ninth United Nations Sustainability Development Goal, i.e., Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure, as it promotes the use of eco-friendly construction practices. Moreover, the present research offers a manifold contribution to the state-of-the-art literature on construction management and offers numerous implications for the construction industry.
Keywords: Recycled concrete aggregates, Silica fume treatment, Fly ash treatment, Water absorption, Workability, Compressive strength
© 2024 Dharmadhikari & Jamkar. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.