

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
DOI: 10.17485/IJST/v13i38.1663
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 38, Pages: 3994-4002
Original Article
Ashutosh Shukla1*, Amit Kumar Chaurasia2, Yasin Mumtaz1, Govind Pandey3
1Graduate Student, University of the Ryukyus Okinawa, Japan. Tel.: +91-740-846-2896
2Graduate Student, Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology Gorakhpur, India
3Professor, Madan Mohan Malaviya University of Technology Gorakhpur, India
*Corresponding Author
Tel: +91-740-846-2896
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:19 September 2020, Accepted Date:05 October 2020, Published Date:24 October 2020
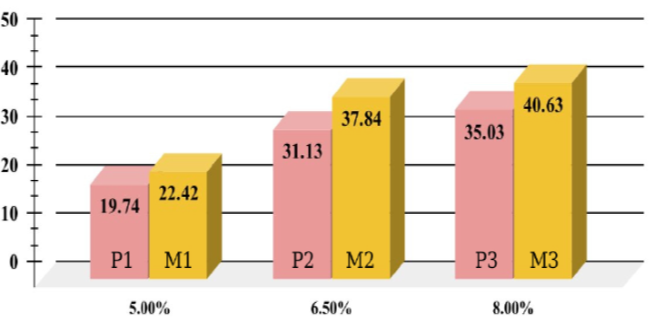
Objective: To analyze the effect of variation of Na2O content on the compressive strength and water absorption of geopolymer paste and mortar specimens. Method: Alkali Activator solution was prepared by mixing sodium silicate solution and sodium hydroxide pellets in appropriate proportions 1 day before its use. The prepared solution was mixed with fly ash (FA) for 5 minutes in Hobart Mixer for geopolymer paste preparation and further sand was mixed to obtain geopolymer mortar. These specimens were placed in a mold and kept in an oven at 48oC for 48 hours. Compressive strength and water absorption tests were conducted on the specimens afterward. In this study, Na2O with 5%, 6.5% & 8.0% was analyzed for its effect on geopolymer paste and mortar.Findings: This research helped in determining the appropriate quantity of NaOH pellets required for geopolymer composite preparation and reducing the cost of construction, as NaOH pellets are more expensive than sodium silicate solution. Maximum compressive strength was achieved by using 8% Na2O content and water absorption was observed maximum at 6% of Na2O content. Novelty: This study is the first of its kind, which has analyzed the effect of Na2O content variation on water absorption and compressive strength of geopolymer paste and mortar specimens.
Keywords: Geopolymer composite; compressive strength; water absorption; Sodium Oxide; fly ash
© 2020 Shukla et al.This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee).
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.