

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2024, Volume: 17, Issue: 26, Pages: 2754-2762
Original Article
Wafa Alharthi1∗, Mohammad Eid Alzahrani1
1Department of Computer Science, Faculty of Computing & Information, Al-Baha University, Al-Baha, Saudi Arabia
*Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:28 February 2024, Accepted Date:18 June 2024, Published Date:06 July 2024
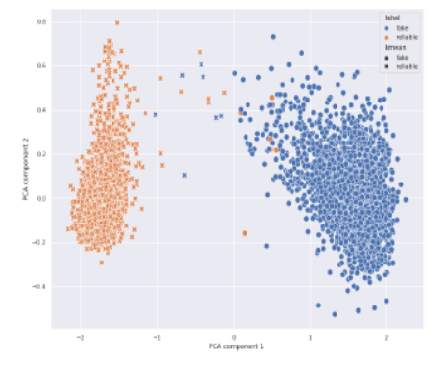
Objectives: The spread of fake news on social media has become a pressing issue in recent times. Despite various organizations' efforts to address this problem, it continues to persist, necessitating finding more effective solutions. This study implements a machine learning-based approach for identifying fake news on social media with improved accuracy. Methods : The study's methodology utilizes a combination of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) to extract semantic features from news articles. Then, a hybrid clustering and classification approach is used, which combines K-means clustering and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) classifiers. Data used is a secondary data consisting of 23481 world news articles obtained from the Reuters.com website and 21417 unreliable news from polifact.com. During the training process, the number of units and layers on the model was tuned to optimize model performance. The model was compared to other baseline models such as KNN, SVM, Decision tree, and Boosted decision tree to establish the best performing model. Findings: The results from the two algorithms were weighted to final classifications using Bayesian probability theory. The proposed approach achieved an accuracy of 99.78%, a sensitivity of 100%, and specificity equal to 99.73%. The model's precision is 99.74%, indicating its ability to identify fake news. The F-score of the approach is 99.87%, indicating that the model strikes a good balance between correctly classifying fake news articles and reliable news articles. The approach outperformed other machine learning classifiers, including KNN, SVM, Decision Tree, and Boosted Decision Tree. Novelty : The study applies a hybrid approach with a classification and clustering algorithm to improve detection of fake news on social media, the approach is tested with varied real-world datasets to establish its robustness under different vocabularies and vocabulary sizes.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Hybrid clustering approach, Classification, CNN, LSTM, Boosted Decision Tree, Social platforms, K-means
© 2024 Alharthi & Alzahrani. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.