

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 12, Pages: 1310-1315
Original Article
P Jasmine1*, Perinba Smith V Robin2
1PhD Scholar, Department of Zoology and Research Centre, Scott Christian College (Affiliated to Manonmaniam Sundaranar University), Nagercoil, 620 003, Tamil Nadu, India
2Head and Associate Professor, Department of Zoology and Research Centre, Scott Christian College (Affiliated to Manonmaniam Sundaranar University), Nagercoil, 620 003, Tamil Nadu, India
*Author for correspondence
P Jasmine
PhD Scholar, Department of Zoology and Research Centre, Scott Christian College (Affiliated to Manonmaniam Sundaranar University), Nagercoil, 620 003, Tamil Nadu, India
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:31 March 2020, Accepted Date:23 April 2020, Published Date:08 May 2020
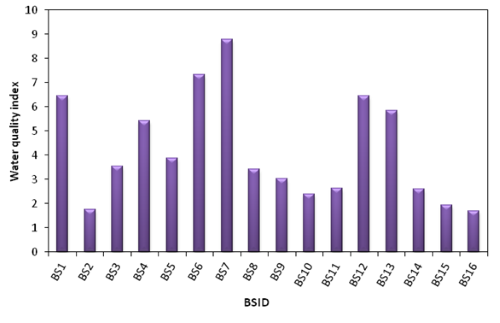
Background/Objectives: Breeding habitat can influence the biological features of the mosquitoes and can be utilized to improve the implementation of the vector control. The major objective of this study was to evaluate the Water Quality Index of various breeding sites. Methods/Statistical analysis: Community Development Blocks (n=9) of the Kanyakumari district were selected as the main research site to study the water quality characteristics of Ae. aegypti mosquitoes' breeding sites. The physicochemical parameters in the mosquito breeding containers were analyzed. Findings: Sixteen types of breeding sites were analyzed, among them nine breeding sites had good quality of water and remaining seven breeding sites contained slightly polluted water. Novelty/Applications: The awareness of water quality parameters of mosquito breeding sites can be used in the adoption of preventive methods.
Keywords: Community development blocks; Physico-chemical parameters; Aedes aegypti; Breeding sites
Copyright: © 2020 Jasmine, Robin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.