

Indian Journal of Science and Technology
Year: 2020, Volume: 13, Issue: 24, Pages: 2491-2501
Original Article
Sanu Meena1*
1Department of Civil Engineering, M.B.M. Engineering College, Jai Narain Vyas University,Jodhpur, 342011, Rajasthan
* Corresponding Author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:18 June 2020, Accepted Date:01 July 2020, Published Date:16 July 2020
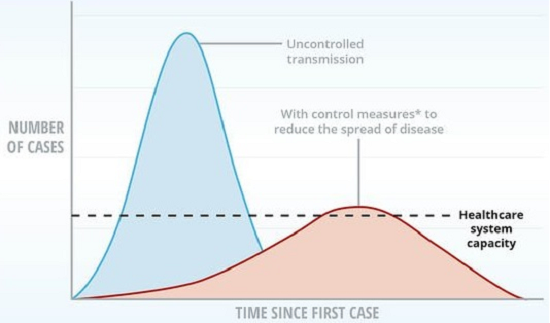
Background: The outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been declared a pandemic by the World Health Organisation (WHO). The outbreak not only affects human health but also travel psychology. Objective and methodology: In order to understand the impact of coronavirus on the travel pattern of Indian people, this study adopts descriptive research techniques to compare travel scenarios during the normal situation, pre-lockdown, and till the COVID-19 pandemic end. The questionnaire included the information for socio-demographic characteristics of the respondents, travel pattern during the normal situation, pre-lockdown and post-lockdown period. The respondent has to perceive the post-lockdown situation and give their responses accordingly. The questionnaire also has some policy-related questions on the five-point Likert scale. Findings: The results of this study are based on online survey responses from 3148 individuals. It is observed that during the prelockdown period, people are more dependent upon the personal mode of transportation and the use of shared mobility dropped (35% compare to the normal situation) significantly because of the high risk of virus transformation from close contact with unknown people and it is expected that, after the end of lockdown period, people will reduce their non-mandatory trips and higher income group will try to avoid travelling in public transport, taxi and other mass transport. This pandemic situation shows us the advantage of walk and bicycle (22% of growth was observed during pre-lockdown), as these modes provides a great way to stay healthy and also an efficient way to support social distancing and reduce the load on public transport. The high percentage of uses of private vehicle (like cars and two-wheeler) will increase congestion on roads and it will lead to more air pollution. The findings of this study will help transport planner and policymakers to plan effective policy strategies to facilitate smooth transportation service during this pandemic situation. The author also recommend the public transport systems to come up with technological upgradation to reduce the contacts in terms of vehicular space (seat arrangements) and automated ticketing and overcrowd warning signals.
Keywords: Coronavirus; COVID-19; travel pattern; lockdown; descriptive analysis
© 2020 Meena.This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Indian Society for Education and Environment (iSee)
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.